Check the clock speed of your CPU.
The easiest way to do this is to open Task Manager and go to the “Performance” tab. The clock speed of your CPU will be listed under “CPU”. If the clock speed is higher than the stock speed, then your CPU is overclocked.
Check the temperature of your CPU. Overclocking can cause your CPU to run hotter, so it’s important to check the temperature regularly. You can use a program like HWMonitor to monitor the temperature of your CPU. If the temperature is too high, you may need to reduce the overclock.
Run a stress test. A stress test is a program that puts your CPU under a heavy load. This can help to identify any instability caused by overclocking. You can use a program like Prime95 or AIDA64 to run a stress test.
Check for errors. If you’re experiencing any errors or crashes, it’s possible that they’re caused by overclocking. Try reducing the overclock or reverting to the stock settings to see if that fixes the problem.
If you’re still having trouble, you can consult with a computer expert or overclocking forum for help.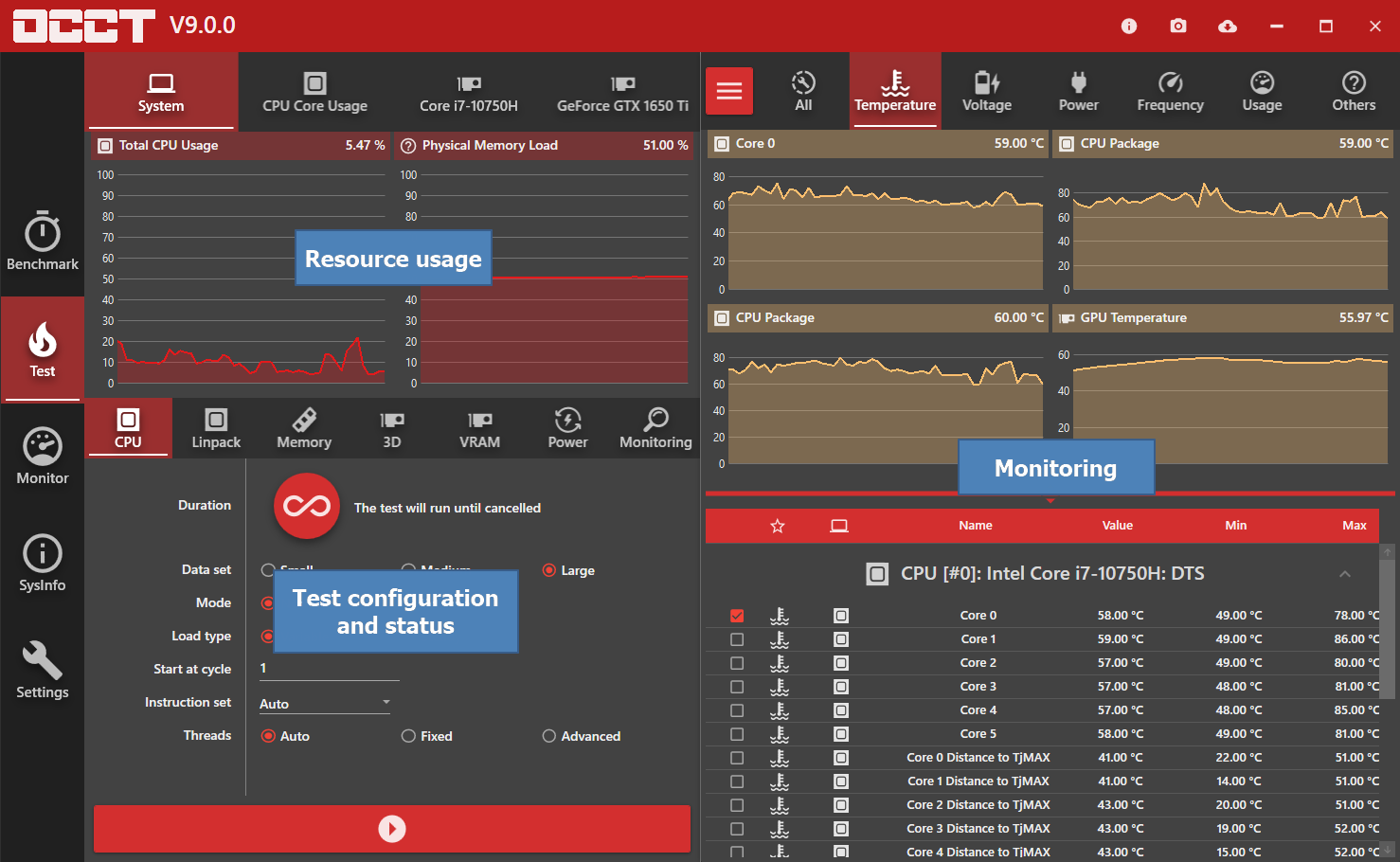
Here are some of the signs of a bad overclock:
Program crashes. As mentioned above, program crashes are a common sign of a bad overclock.
Blue screens of death. A blue screen of death (BSOD) is a serious error that can cause your computer to crash. If you’re getting BSODs, it’s possible that they’re caused by overclocking.
Stuttering or freezing. Overclocking can sometimes cause your computer to stutter or freeze.
High temperatures. As mentioned above, overclocking can cause your CPU to run hotter. If the temperature gets too high, it can damage your CPU.
If you’re experiencing any of these problems, it’s a good idea to reduce the overclock or revert to the stock settings.
